A collaborative Nature paper between VINSE faculty member Sokrates Pantelides and authors in Singapore & Tokyo was published this week.
Experiments into amorphous carbon monolayer lend new evidence to physics debate
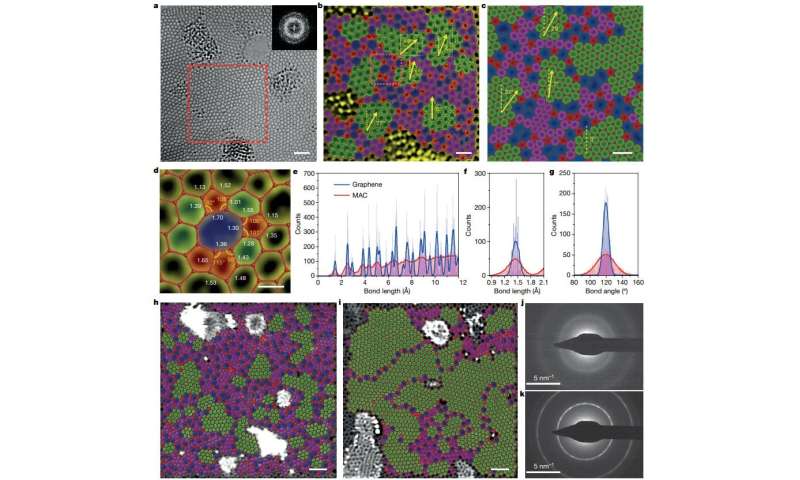
Plastic, glass and gels, also known as bulk amorphous materials, are everyday objects to all of us. But for researchers, these materials have long been scientific enigmas—specifically when it comes to their atomic makeup, which lacks the strict ordered structure of crystals found in most solids such as metals, diamonds and salts.
Although generally believed by the scientific community to be continuous random networks of atoms, a long-standing, fundamental question existed: Are amorphous materials truly continuous random networks or do they have nanocrystallites embedded within them?
Full article: Here
