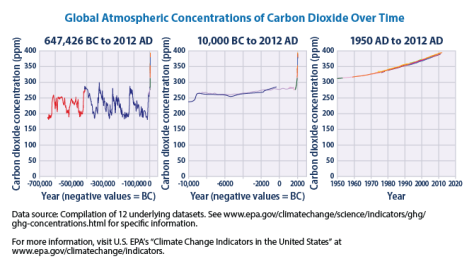
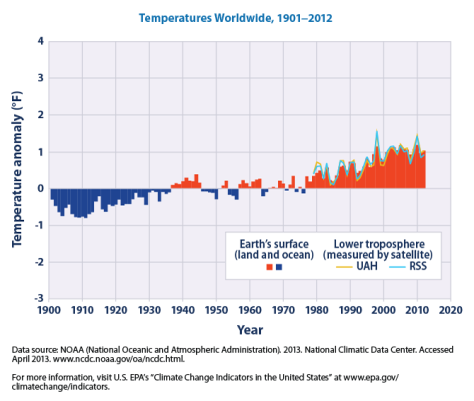
Last month an asteroid in orbiting between Saturn and Uranus was discovered to hang a ring system. This asteroid is named Chariklo, and is part of a class of solar system bodies known as centaurs, which are thought o have originated in the Kuiper belt. The rings are thought to have formed after some slow solar system collision scattered debris around Chariklo. The reason the collision must have been slow is that Chariklo is very small and thus has little gravity, and faster moving objects would have escaped its force of gravity quite easily. Besides being quite a shock, this could never happen in the inner solar system near the asteroid belt. This is because the asteroid belt and inner planets are much more affected by solar wind, and if Chariklo were in that region the solar wind would have blown the tiny ring particles away. What they have not yet discovered is the shepherd moons, which scientists believe is the only explanation to rings forming on such a small system. A shepherd moon confines the small particles in orbit and is thought to be about as massive as both rings combined. The other possible option is that the rings are very young and time has not spread them out as expected.
February 2026 S M T W T F S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Archives
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- July 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
Currently Used Categories
Tag Cloud
- astro201
- astro2110
- astrobiology
- astronomy
- blog1
- blog2
- blog3
- blog4
- blog5
- blog6
- blog7
- blog8
- blog9
- blog10
- brahe
- Class
- Comets
- Copernicus
- earth
- Europa
- extremophiles
- galilei
- galileo
- gravity
- history
- HW2
- HW6
- jupiter
- Kepler
- life
- Mars
- me
- Moon
- NASA
- Newton
- planets
- pluto
- saturn
- Solar System
- space
- technology
- telescopes
- tides
- Time
- Uncategorized