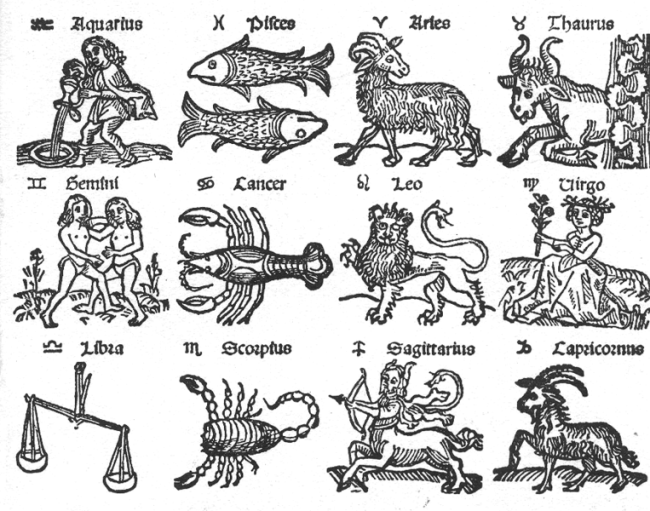
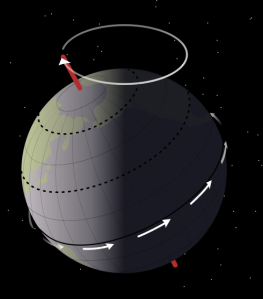
The Zodiac was created about 2,000 years ago as a way to track time. Each month, the sun appears to pass through 1 of 12 constellations that are each tied to a sign (In 1930, the International Astronomical Union, actually defined 13 constellations that the Sun passes through, but one does not have a sign). These constellations define the zodiac. The Sun and the constellations do not actually move, but Earth’s orbit around the Sun creates the illusion that the Sun is moving against the background of stars. It takes about a month for the Sun to pass through each constellation, and those days are assigned an astrological sign, which are the basis for horoscopes. For hundreds of years, many people have thought that the constellation passing through the sun on their birthday (your astrological sign) says something about your personality. But nowadays your astrological sign, does not necessarily correspond with the constellation that was near the Sun on your birthday. The constellations appear to have shifted. This is because over time the moon’s gravitational pull on the Earth has caused it to wobble on its axis, which is called precession. Precession makes the earth move similarly to how a top does. The Earth slightly wobbles as it rotates around its axis, tracing a circle in the sky, so the poles are not always pointing exactly to the same background stars. Although the wobble is very slow—it takes about 26,000 years to complete a full wobble circle—the movement affects the apparent location of the stars we see. Since it has been about 2,000 years since the zodiac signs were created, the corresponding constellations have shifted about a month. 2,000 years from now the signs will be 2 months off the constellation that can actually be seen in the sky. Due to Earth’s constant precession, the astrological signs will continue to get further off track from their corresponding constellation, but the zodiac constellations do help us track all of Earth’s movement.
February 2026 S M T W T F S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Archives
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- July 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
Currently Used Categories
Tag Cloud
- astro201
- astro2110
- astrobiology
- astronomy
- blog1
- blog2
- blog3
- blog4
- blog5
- blog6
- blog7
- blog8
- blog9
- blog10
- brahe
- Class
- Comets
- Copernicus
- earth
- Europa
- extremophiles
- galilei
- galileo
- gravity
- history
- HW2
- HW6
- jupiter
- Kepler
- life
- Mars
- me
- Moon
- NASA
- Newton
- planets
- pluto
- saturn
- Solar System
- space
- technology
- telescopes
- tides
- Time
- Uncategorized