Efficient Quality Control with Mixed CT and CTA Datasets
Lucas W. Remedios, Leon Y. Cai, Colin B. Hansen, Samuel W. Remedios, Bennett A. Landman (2022). Efficient Quality Control with Mixed CT and CTA Datasets. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022.
Abstract
Deep learning promises the extraction of valuable information from traumatic brain injury (TBI) datasets and depends on efficient navigation when using large-scale mixed computed tomography (CT) datasets from clinical systems. To ensure a cleaner signal while training deep learning models, removal of computed tomography angiography (CTA) and scans with streaking artifacts is sensible. On massive datasets of heterogeneously sized scans, time-consuming manual quality assurance (QA) by visual inspection is still often necessary, despite the expectation of CTA annotation (artifact annotation is not expected). We propose an automatic QA approach for retrieving CT scans without artifacts by representing 3D scans as 2D axial slice montages and using a multi-headed convolutional neural network to detect CT vs CTA and artifact vs no artifact. We sampled 848 scans from a mixed CT dataset of TBI patients and performed 4-fold stratified cross-validation on 698 montages followed by an ablation experiment—150 stratified montages were withheld for external validation evaluation. Aggregate AUC for our main model was 0.978 for CT detection, 0.675 for artifact detection during crossvalidation and 0.965 for CT detection, 0.698 for artifact detection on the external validation set, while the ablated model showed 0.946 for CT detection, 0.735 for artifact detection during cross-validation and 0.937 for CT detection, 0.708 for artifact detection on the external validation set. While our approach is successful for CT detection, artifact detection performance is potentially depressed due to the heterogeneity of present streaking artifacts and a suboptimal number of artifact scans in our training data.
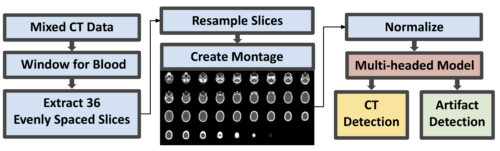
units), converted into a 2D montage from resampled axial slices and normalized. A multitask deep learning model then
simultaneously performs two classifications: CT vs CTA and artifact vs no artifact.